| |
 |
| Fig. 1 |
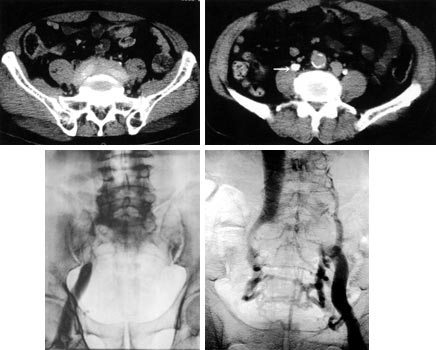
 Computed tomography showed the retroperitoneal
tumor sorrounding the bilateral iliac vessels (A), and a remarkable
dilation of right ureter (B). Venography showed total occlusion
of the right external iliac (C) and left common iliac veins (D),
and poor collaterals in right-side venous drainage. Computed tomography showed the retroperitoneal
tumor sorrounding the bilateral iliac vessels (A), and a remarkable
dilation of right ureter (B). Venography showed total occlusion
of the right external iliac (C) and left common iliac veins (D),
and poor collaterals in right-side venous drainage. |
|
| |
 |
| Fig. 2 |
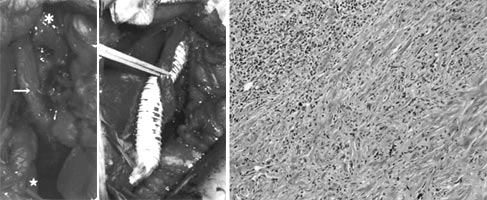
 Operative fidings showed the tumor firmly surrounding
the right iliac vessels and ureter (arrow, A). Venous bypass
was performed between external iliac vein (A) and inferior vena
cava (B) as well as ureterolysis. Pathlogical fidings of the
tumor (C) showed chronic inflammatory cell infiltration consisting
of plasma cells and lymphocytes along with a proliferation of
collagen fibers (hematoxylin eosin stain). Operative fidings showed the tumor firmly surrounding
the right iliac vessels and ureter (arrow, A). Venous bypass
was performed between external iliac vein (A) and inferior vena
cava (B) as well as ureterolysis. Pathlogical fidings of the
tumor (C) showed chronic inflammatory cell infiltration consisting
of plasma cells and lymphocytes along with a proliferation of
collagen fibers (hematoxylin eosin stain). |
|
| |
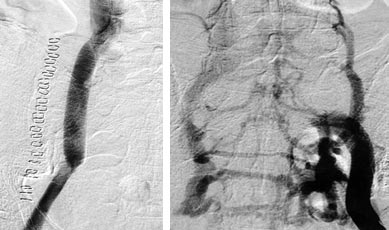 |
| Fig. 3 |
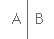 Postoperative venography showed a patent ePTFE
graft (A), and a good venous drainage from the left-side iliac
veins (B). Postoperative venography showed a patent ePTFE
graft (A), and a good venous drainage from the left-side iliac
veins (B). |
|
|


